How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood
How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood
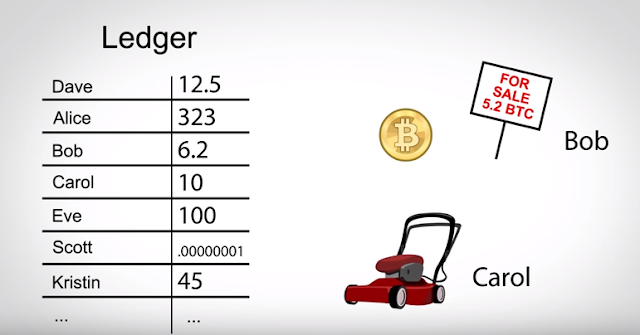
at a very basic level bitcoin is just a digital file or ledger that contains names and balances and people exchanged money by changing this file when Bob sells Carol a lawnmower for 5.2 bitcoins Bob's balance goes up by 5.2 and Carol's down by 5.2 there's no gold or government-issued money backing these numbers Bob is only willing to trade his real-life lawnmower for a higher number in this digital file because he is faith that other people
will also trust the system so who maintains this ledger and make sure no one cheats when goal of Bitcoin is to avoid any centralized control so every participant maintains their own copy of the ledger one surprising consequence of this is that everyone can see everyone else's balances although the real system only uses account numbers and not names so there's some level of anonymity if everyone maintains their own ledger how are all the Ledger's kept in sync as money is transferred at a basic level when you want to send money you simply tell everyone else by broadcasting a message with your account number the
receivers and the amount everyone across the entire world then updates their ledger as a quick aside I'm describing how Bitcoin works for power users people who help maintain the system you can also just use the system to send and receive money though without maintaining a ledger if sending money is as simple as creating a message with some account numbers what's to stop a thief Alice from spending Bob's money by using his account number like a pen and paper check the coin requires a kind of signature to prove that the sender is the real owner of an account but it's based on math rather than handwriting when a new account number is
created it comes along with a private key mathematically linked to that account number if you've heard of a Bitcoin wallet these keys are what it holds and are what allow you to create signatures to create a signature a private key and the text from a transaction are fed into a special cryptographic function another function allows other people to check the signature making sure it was created by the account owner and that it applies to that specific transaction unlike the handwritten version these signatures can't be copied and reused in the future as they're unique to each transaction while the mathematical signatures prove who sent a transaction they can't prove when it was sent and this turns out to be problematic in our traditional banking system if Alice wrote two checks
How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood
but only had enough money to cover one of them the bank would pay the first person attempting the cash is checked but refused the second because alice's account would be empty so the order of these checks is critical because it determines who should get paid unfortunately order is much harder to determine in Bitcoin where instead of a single bank there are individuals all over the world network delays might cause transactions to arrive in different orders in different places and fraudsters could lie about time stamps two recipients might both think their transaction is
first and ship a product effectively allowing Alice to spend money twice Bitcoin prevents this by providing a way for the entire world to decide on transaction order as new transactions are created they go into a pool of pending transactions and from here they'll be sorted into a giant chain that locks in their order to select which transaction is next a kind of mathematical lottery is held participants select a pending transaction of their choice and begin trying to solve a special problem that will link it to the end of the chain the first person to find a solution wins and gets to have their transaction selected as next in the chain so what's this linking problem it's based on a special function called a cryptographic hash as scary as this sounds it just
mixes up its inputs and spits out a number but it's special because it's irreversible there's no easy way to start with an output and then find an input that generates it other than by making lots of guesses and this is literally what people are doing in Bitcoin feeding this function random numbers until the output meets certain criteria besides a random guess you also input a transaction from the pending pool and chain which is where the linking part comes in so the latter I provides a way for the entire world to decide which transaction is next but the math behind it also helps ensure everyone agrees about past transactions to suppose you're joining the network for the first time and request a copy of the transaction chain to get caught up but receive several different versions which one should you trust ideally you would trust the one that the majority of people
are using but determining this on the internet is difficult what would stop a single person from voting millions of times Bitcoin prevents this by requiring people to solve math problems to vote this causes each vote to have a cost in computing power making it unlikely that a single person or group could ever afford to out vote or out compute the majority of users the transaction ordering process described before actually provides the voting system part of the
input to the linking problem is a transaction from the end of a chain so each gas is effectively a vote for that chain but how are all the votes tallied because the cryptographic hash function has well-defined statistical properties you can look at any given answer and estimate how many guesses it took to find it just like estimating how many coin flips it would take to get 100 heads in a row so the links in a chain not only put transactions in order but also act as an effective vote tally making it easy to see which chain most people are using finally
how does money get created every time someone wins the lottery to pick the next transaction in the chain new bitcoins are created out of thin air and awarded to their account solving these problems is commonly called mining as this is how money enters the system but the main purpose of the math is to make sure everyone's Ledger's agree the math simply provides a convenient way to randomly distribute money into the world in fact sometime around twenty one forty no more money will be created and participants will only be paid from fees added on to transactions I hope this gives you a quick sense for how Bitcoin works if you'd like a more detailed summary check out my 22 minute video how Bitcoin works under the hood
How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood
How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood

0 Response to "How Bitcoin Encryption (works) For Beginners Under the Hood"
Post a Comment